Select your destination
Continue to Radiometer Medical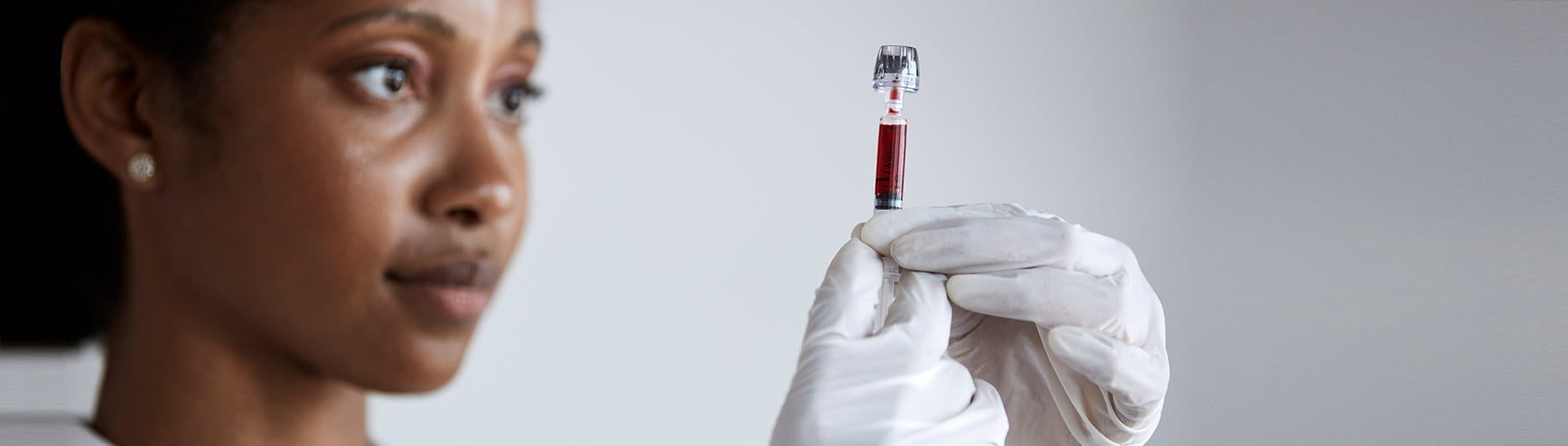
Blood gas syringes and capillary tubes
Meet your blood sampling needs with our samplers, designed to facilitate reliable test results
Syringes and capillary tubes are designed to reduce the risk of preanalytical errors
As blood gas specialists, we’re empowered to advance acute care diagnostics. From reducing the risk of preanalytical errors to providing a reliable blood gas test result, we ensure constant focus on supporting you and your patients.
Radiometer capillary tubes, aspirating and self-fill blood gas syringes are designed with various features that are intended to reduce the risk of preanalytical errors.
Furthermore, our products support the Patient Blood Management which is an evidence-based approach to optimizing the care of patients’ blood. This includes opportunities to minimize blood loss and avoid the inappropriate use of blood.
We’re committed to empowering you to take control of the blood sampling process. Discover blood gas syringes or capillary tubes that support your blood sampling workflow.
Our blood gas syringes and capillary tube
Explore the syringes and capillary tube that can meet your needs
![]()
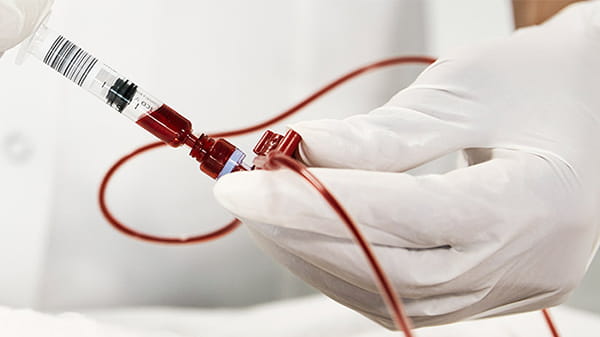
Aspirating syringe
Pre-barcoded aspirating syringe helps ensure correct patient-sample identification every time when using with a Radiometer blood gas analyzer with 1st Automatic.
![]()
Self-fill syringe
safePICO self-fill syringe is equiped with an integrated mixing ball and automatic mixing which enhances analytical quality through standardized mixing, without causing hemolysis.
![]()
Capillary tubes
Our capillary tubes are used for low-volume blood gas sampling, mainly on neonates.
 Specialists by blood
Specialists by blood
The history of Radiometer as we know it today began in 1954 when Radiometer developed the world’s first commercially available blood gas analyzer. Since then, we have refined our blood gas testing knowledge and experience and continue to advance our acute care diagnostic solutions.
Minimizing preanalytical errors in blood gas testing
Increase patient care with proper sampling technique in the preanalytical phase
Hemolysis in blood samples
Reducing hemolysis in blood samples
Hemolysis is the rupture of the red blood cells, and may happen during sample collection and the following process. The rupture causes the intracellular components of the destroyed red blood cells to be mixed with the plasma. Some of the components, e.g., potassium (K+), are more concentrated in the intracellular compartment than in the plasma phase. Therefore, the reported potassium result will be falsely high.
Clots in blood samples
Air bubbles in the sample
Air bubbles in the sample
Room air contamination of a blood gas sample may alter the values of the sample so that it no longer represents patient's status.
To minimize errors:
- Visually inspect the sample for air bubbles
- Expel any bubbles by gently tapping the sides of the syringe right after sampling and before mixing
- Use arterial blood gas syringes with tip caps that are vented and will allow you to expel air and seal the syringe without getting in contact with blood
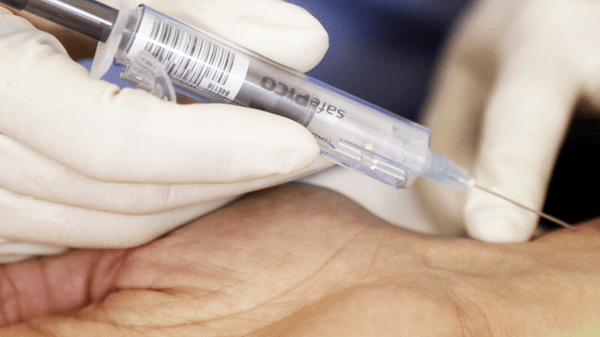
Needlestick injuries
![]()
Needlestick injuries
Needlestick injury and unwanted contact with patient blood are daily risks for operators collecting blood gas samples.
To minimize risks
- If available, use a safety device that limits the risk of contact with patient blood
- Do not recap needles
- If available, use a needle shield protection device when removal of needles
- Ensure a dedicated procedure for operator safety is established and followed in your facility
Mix-up of patient samples
![]()
Preanalytical blood gas handbook
Radiometer blood gas syringes and capillary tube
Syringes and capillary tube used in your hospital
Related knowledge sources
![]()
Patient blood management
Patient Blood Management is an evidence-based approach to optimizing the care of patients’ blood. This includes opportunities to minimize blood loss and avoid the inappropriate use of blood.

How-to videos - guide to blood gas
Watch six educational videos to support you in understanding blood gas analysis.
![]()
Mastering the preanalytical phase
Learn about 12 common preanalytical errors and how to avoid them and test your self with a quiz.
Cookies are used on this website
Use of cookiesPlease enter a valid email
We will be sending an e-mail invitation to you shortly to sign in using Microsoft Azure AD.
It seems that your e-mail is not registered with us
Please click "Get started" in the e-mail to complete the registration process
Radiometer is using Microsoft AZURE Active Directory to authenticate users
Radiometer uses Azure AD to provide our customers and partners secure access to documents, resources, and other services on our customer portal.
If your organization is already using Azure AD you can use the same credentials to access Radiometer's customer portal.
Key benefits
- Allow the use of existing Active Directory credentials
- Single-sign on experience
- Use same credentials to access future services
Request access
You will receive an invitation to access our services via e-mail when your request has been approved.
When you accept the invitation, and your organization is already using AZURE AD, you can use the same credentials to access Radiometer's customer portal. Otherwise, a one-time password will be sent via e-mail to sign in.